
| CV | Google Scholar | Github | Linkedin | |
I am a first-year CS Ph.D. student at Stony Brook University working with Prof. Dimitris Samaras at CVLab.
My research interests lie in the field of Computer Vision, with a focus on generative modeling and visual synthesis.
|

SBU |

Academia Sinica |

UIUC |
NCTU |
|---|
|

|
| abstract | arXiv |
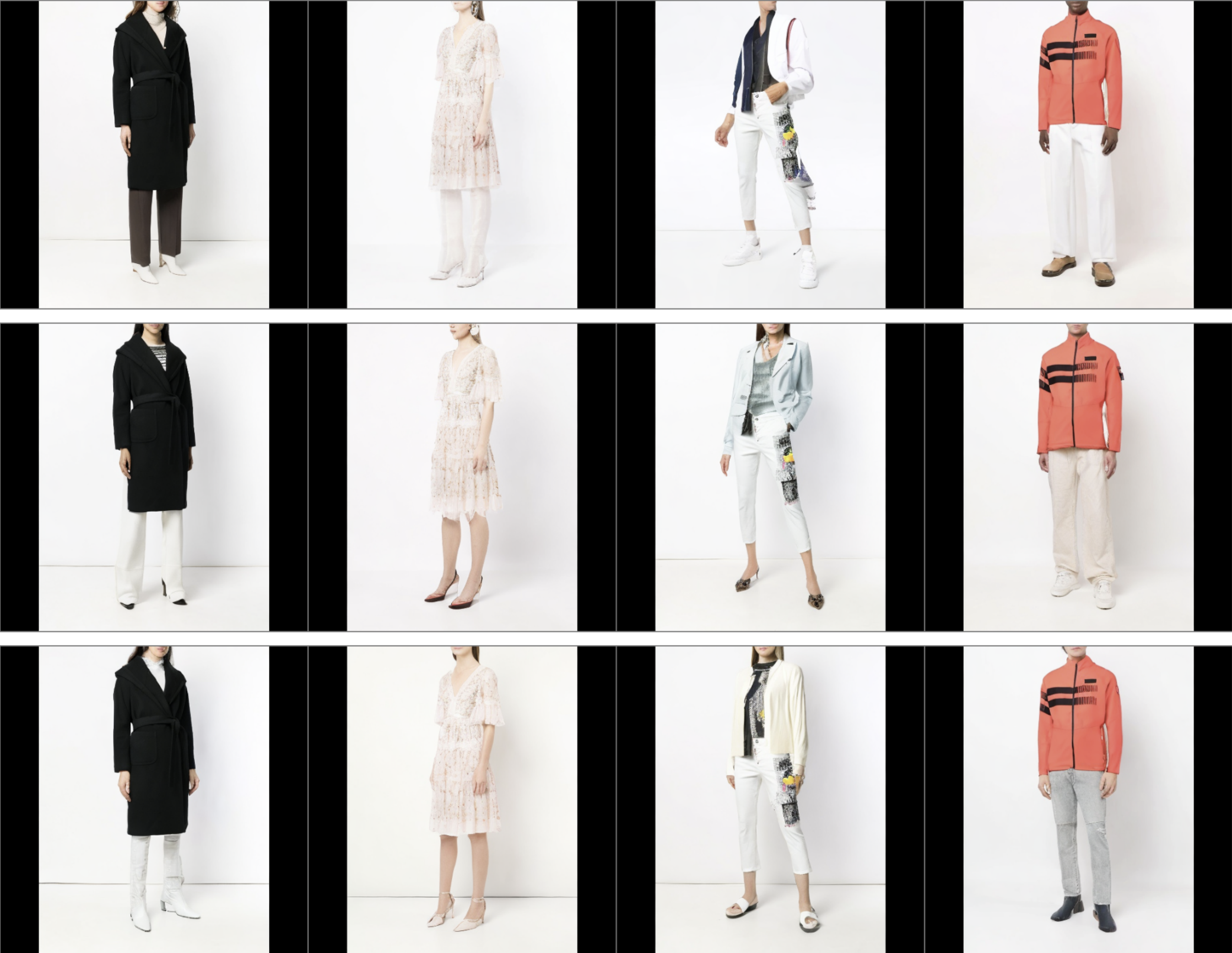
Virtual Try-on (VTON) involves generating images of a person wearing selected garments. Diffusion-based methods, in particular, can create high-quality images, but they struggle to maintain the identities of the input garments. We identified this problem stems from the specifics in the training formulation for diffusion. To address this, we propose a unique training scheme that limits the scope in which diffusion is trained. We use a control image that perfectly aligns with the target image during training. In turn, this accurately preserves garment details during inference. We demonstrate our method not only effectively conserves garment details but also allows for layering, styling, and shoe try-on. Our method runs multi-garment try-on in a single inference cycle and can support high-quality zoomed-in generations without training in higher resolutions. Finally, we show our method surpasses prior methods in accuracy and quality. |

|
| abstract |
project page | arXiv |
We present a diffusion-based video editing framework, namely DiffusionAtlas, which can achieve both frame consistency and high fidelity in editing video object appearance. Despite the success in image editing, diffusion models still encounter significant hindrances when it comes to video editing due to the challenge of maintaining spatiotemporal consistency in the object's appearance across frames. On the other hand, atlas-based techniques allow propagating edits on the layered representations consistently back to frames. However, they often struggle to create editing effects that adhere correctly to the user-provided textual or visual conditions due to the limitation of editing the texture atlas on a fixed UV mapping field. Our method leverages a visual-textual diffusion model to edit objects directly on the diffusion atlases, ensuring coherent object identity across frames. We design a loss term with atlas-based constraints and build a pretrained text-driven diffusion model as pixel-wise guidance for refining shape distortions and correcting texture deviations. Qualitative and quantitative experiments show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in achieving consistent high-fidelity video-object editing. |

|
| abstract |
project page |
paper |
Retail photography imposes specific requirements on images. For instance, images may need uniform background colors, consistent model poses, centered products, and consistent lighting. Minor deviations from these standards impact a site's aesthetic appeal, making the images unsuitable for use. We show that Stable Diffusion methods, as currently applied, do not respect these requirements. The usual practice of training the denoiser with a very noisy image and starting inference with a sample of pure noise leads to inconsistent generated images during inference. This inconsistency occurs because it is easy to tell the difference between samples of the training and inference distributions. As a result, a network trained with centered retail product images with uniform backgrounds generates images with erratic backgrounds. The problem is easily fixed by initializing inference with samples from an approximation of noisy images. However, in using such an approximation, the joint distribution of text and noisy image at inference time still slightly differs from that at training time. This discrepancy is corrected by training the network with samples from the approximate noisy image distribution. Extensive experiments on real application data show significant qualitative and quantitative improvements in performance from adopting these procedures. Finally, our procedure can interact well with other control-based methods to further enhance the controllability of diffusion-based methods. |
|
| abstract |
paper |
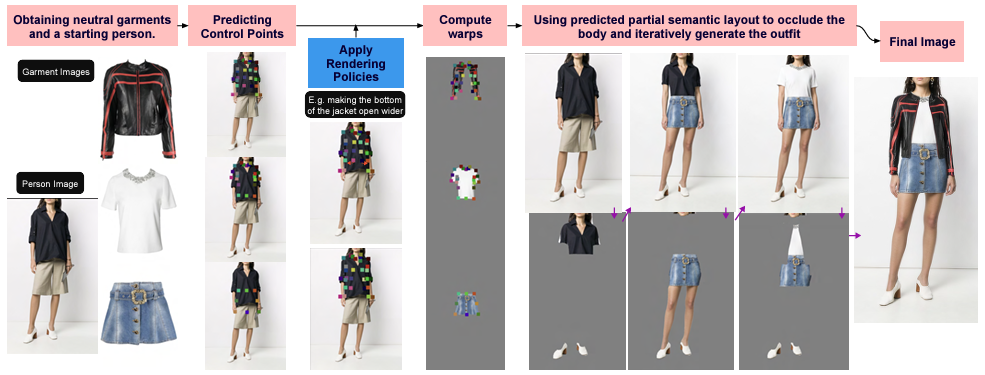
This paper shows how to impose rendering policies on a virtual try-on (VTON) pipeline. Our rendering policies are lightweight procedural descriptions of how the pipeline should render outfits or render particular types of garments.
Our policies are procedural expressions describing offsets to the control points for each set of garment types.
The policies are easily authored and are generalizable to any outfit composed of garments of similar types.
We describe a VTON pipeline that accepts our policies to modify garment drapes and produce high-quality try-on images with garment attributes preserved.
|
|
| abstract |
paper |
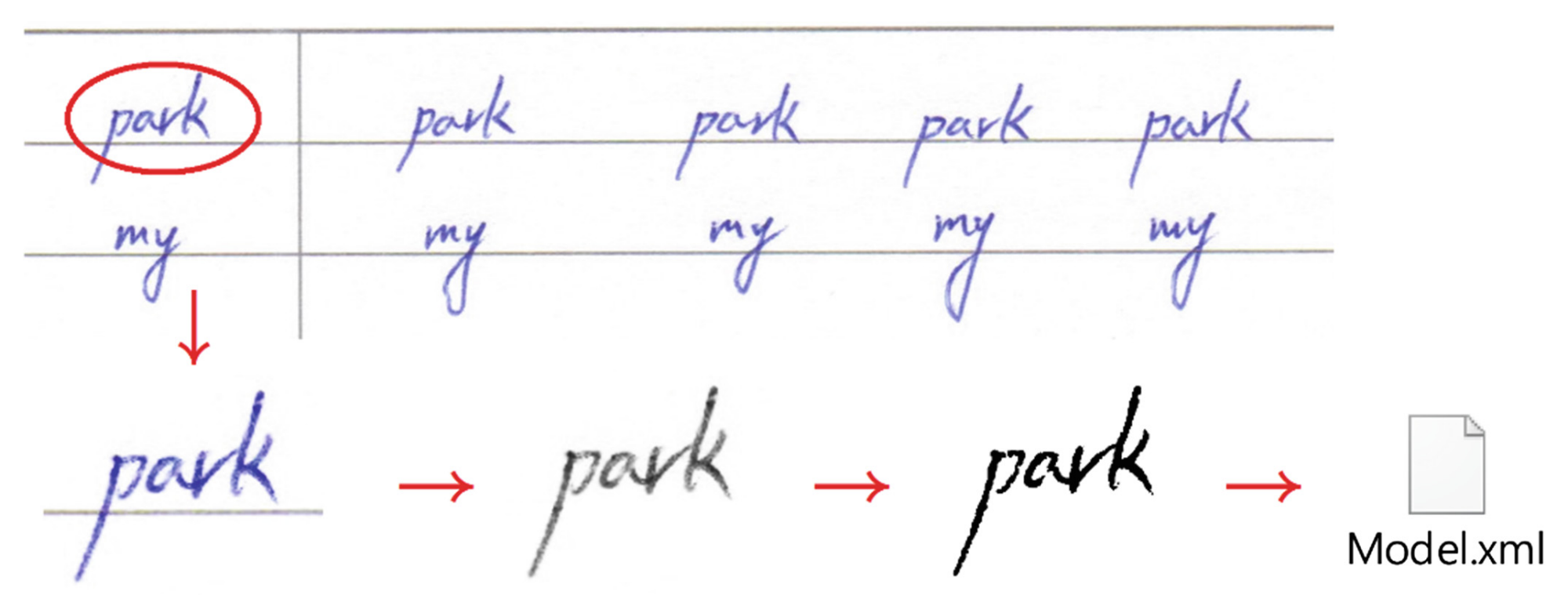
Educational materials play a vital role in effectively conveying information to learners, with the readability and legibility of written text serving as crucial factors. This study investigates the influence of font selection on educational materials and explores the relationship between handwriting fluency and cognitive load. By identifying challenges in written expression, such as reduced working memory capacity, text organization difficulties, and content recall issues, the study sheds light on the significance of neat handwriting. The research emphasizes the relevance of neat handwriting in critical examinations, including college entrance exams, academic English exams, and job interviews, where the fluency of one’s handwriting can impact the decision-making process of interviewers. This highlights the value of handwriting fluency beyond educational contexts. Advancements in computer science and machine vision present new opportunities for automating font evaluation and selection. By employing machine vision algorithms to objectively analyze visual features of fonts, such as serifs, stroke width, and character spacing, the legibility and readability of fonts used in English language teaching materials are assessed. In this study, machine vision techniques are applied to score fonts used in educational materials. The OpenCV computer vision library is utilized to extract visual features of fonts from images, enabling the analysis of their legibility and readability. The primary objective is to provide educators with an automated and objective tool for scoring handwriting, reducing visual fatigue, and ensuring impartial evaluations. This research contributes to enhancing the quality of educational materials and provides valuable insights for educators, researchers, and font designers. |

|
| abstract |
poster |
Spectral indices are combinations of the pixel values from two or more spectral bands in a multispectral image. Spectral indices are used to highlight pixels showing the relative abundance or lack of a land-cover type of interest in an image. This study aims to build a feature space with some spectral indices and see if those indices are useful and efficient for the classification of satellite images. The training data is extracted from the NAIP program with six classes (building, barren land, trees, grassland, road, and water). Each image has four spectral bands (RED, GREEN, BLUE, and NIR). After some comparison and analysis, the spectral indices used are Modified Soil-adjusted Vegetation Index (MSAVI), Atmospherically Resistant Vegetation Index (ARVI), Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), Difference Spectral Building Index (DSBI), and Road Extraction Index (REI). With these spectral indices and the distribution of the four spectral bands (here, we use mean and standard deviation to represent each distribution), an 18-dimensional feature space is formed. The dimensionality of the feature space is then reduced to improve the classification accuracy using the Unsupervised Feature Selection with Ordinal Locality (UFSOL). The spectral indices have performed a good job as features and has attained 92.58% of accuracy. |

|
|

|
|
|
Thanks for this template. |